Communicable
or infectious diseases are infections which are transmitted from an infected
person, animal or reservoir to another person. These infections can spread
through direct or indirect contact. Knowledge of how infectious diseases spread
can help minimize the risk of infections. Adopting disease prevention measures
can reduce illness.
Disease prevention focuses on prevention strategies in
reducing the risk of developing diseases and other morbidities. “Prevention
is better than cure”. According to this, suitable preventive measure must be
taken for the occurrence and spread of diseases. The concept of prevention of
diseases includes three levels.
A.
PRIMARY
PREVENTION:
Primary
prevention may be defined as” the action taken prior to the onset of disease
which removes the possibility of ever occurrence of a disease”. Primary
prevention is studied under two sub categories
These
include:
·
Maintenance of a healthy environment
·
Maintenance of personal hygiene
·
Eating adequate balanced diet
·
Provision for safe water supply
·
Provision of proper disposal of human excreta
and domestic wastes
·
Provision of well managed sewer system
·
Isolation of infected persons
·
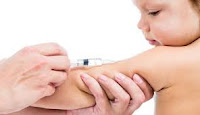
Immunization
·
Maintenance of healthy and clean sex life
·
Motivating people to avoid the use of
tobacco, alcohol and drugs.
ii.
Specific
protective measures
Specific
diseases can be prevented by taking specific measures against these diseases.
Ex: tuberculosis, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, polio, measles etc, can be
prevented by immunization at proper age and time. Since children are more susceptible
to these diseases. Hence vaccination is necessary. Few diseases like Rickets
and scurvy can be prevented by administration of vitamin D and vitamin C
respectively.
Similarly
industrial accidents can be prevented by using specific protective devises like
goggles, gloves, shield against carcinogens, allergens and occupational hazards
etc.
Primary
prevention also includes prevention of chronic diseases by avoiding smoking,
drinking, dietary control and physical exercise etc.
Primary
prevention is less expensive, safe and more effective way of preventing
diseases in comparison to secondary and tertiary prevention.
B.
SECONDARY
PREVENTION
Secondary prevention aims to detect new
cases of infectious disease at the earliest possible stage and intervene in
ways that prevent or reduces the risk of infection spreading further in
population. Secondary prevention strategies include:
i.
Early
treatment
This
level of prevention involves infected (or exposed) individuals receiving early
treatment to prevent the transmission of pathogens to susceptible hosts.
Benefit to the individual may also result from treatment, but the aim of
community health is to protect the community as a whole from further
infections, rather than to aid the personal recovery of identified patients.
ii.
Education
and health-related behavior modification
 Secondary
prevention relies partly on educating the population about signs of illness
that require prompt medical appointment coupled with systematic surveillance to
detect and report cases quickly and respond with effective treatment. If the
disease has the potential to generate an epidemic, it is necessary to isolate
(quarantine) infected individuals by educating about how they can prevent or
reduce the risk of transmission to other individual.
Secondary
prevention relies partly on educating the population about signs of illness
that require prompt medical appointment coupled with systematic surveillance to
detect and report cases quickly and respond with effective treatment. If the
disease has the potential to generate an epidemic, it is necessary to isolate
(quarantine) infected individuals by educating about how they can prevent or
reduce the risk of transmission to other individual.
iii.
Screening
Infected
individuals can also be identified even before symptoms develop in systematic screening
programmes, i.e. application of a test or an investigation to
large numbers of individuals to identify who are at risk of developing a
particular disease, or in case of infectious disease those who are already
infected. The screening service can target groups assumed to be at high risk.
Ex: TB screening.
C. TERTIARY
PREVENTION
 Medical
treatment to prevent the worst outcomes of a disease in an individual is known
as tertiary prevention. The aim of the tertiary prevention is
to reduce further complications or permanent disability in patients which includes
Medical
treatment to prevent the worst outcomes of a disease in an individual is known
as tertiary prevention. The aim of the tertiary prevention is
to reduce further complications or permanent disability in patients which includes- Permanent disability can be prevented by immunizing the infants against polio, etc. Disability due to industrial accidents can be prevented by wearing goggles, gloves, hood etc. Surgical operations can limit the disability to the extent. Adequate treatment and physiotherapy can reduce the duration of disability.
- Rehabilitation of the handicapped patients is very important which could be brought by medical(physiotherapy), social, educational and vocational rehabilitation, sheltered workshops, colonies, selective changes in occupation, opening hostels and schools for handicapped children and attachment of artificial limbs to an accident victims etc.
The
key goal for tertiary prevention is to enhance quality of life.




No comments:
Post a Comment